


Automotive HVAC Systems: Core Components & Key Parts
Traditional Engine-Driven System
Utilizes engine power for compression
Dominates in fuel-powered vehicles
Electric Compressor System
Powered by high-voltage battery
Essential for electric/hybrid vehicles
Heat Pump System
Reversible refrigeration cycle (cooling/heating)
Emerging solution for EV range efficiency
| Component | Function | Key Terms |
|---|---|---|
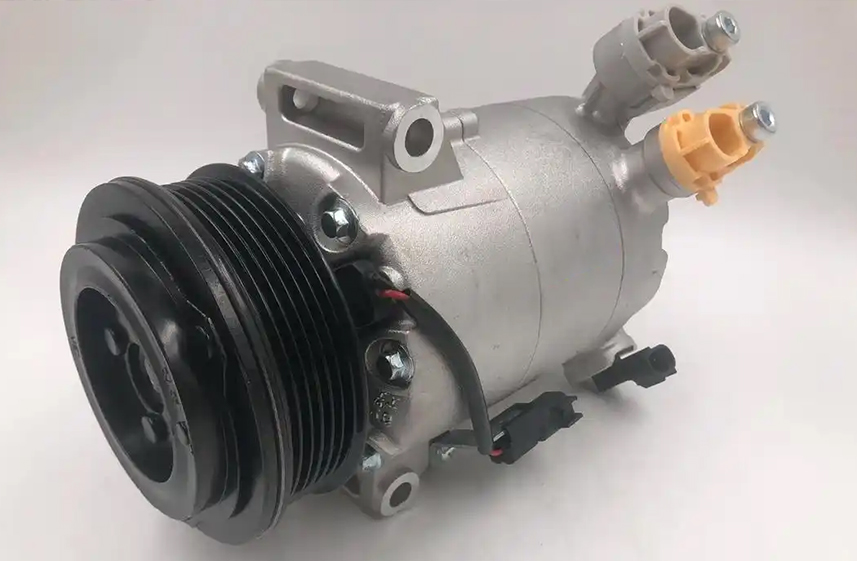
| Compressor | Pressurizes refrigerant | Swash plate / Scroll type |
| Condenser | Dissipates heat (gas→liquid) | Microchannel / Tube-fin |
| Expansion Valve | Regulates refrigerant flow | TXV / Electronic EXV |
| Evaporator | Absorbs cabin heat (liquid→gas) | Plate-fin / Laminate |
| Receiver-Drier | Filters moisture/debris | Desiccant bag / Sight glass |
Heater Core
Uses engine coolant heat (80–100°C) for cabin warming
PTC Heater
Electric heating element for EVs (instantly warms air/coolant)
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Blower Motor | Drives airflow (ECM motors for variable speed) |
| Actuators | Controls air mix/defrost/direction flaps |
| Cabin Filter | Particulate/pollen filtration (HEPA upgradeable) |
Sensors: Ambient/cabin temp, evaporator frost, sunlight
ECU: Processes data to manage compressor clutch/PTC/actuators
Integrated Thermal Management
Combines HVAC with battery/motor cooling (e.g., Tesla Octovalve)
CO₂ (R744) Systems
Environmentally friendly refrigerant for heat pumps
Compressors: Denso, Valeo, Hanon
Heat Exchangers: Mahle, Modine
Controls: Bosch, Continental
Industry Insight: EV thermal systems consume 15–30% of battery energy. Next-gen heat pumps aim to reduce this by 40% through waste heat recovery.